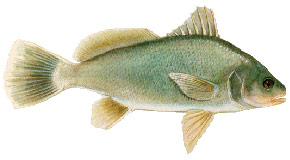
Lepomis, the generic name, is Greek and means “scaled gill cover.” The species epithet microlophus is Greek for “small nape.” The redear is a deep-bodied sunfish with a relatively small mouth. Color ranges from dark olive green above to almost white on the belly. The sides are usually yellow to green. The spinous dorsal fin, which is anterior to the soft dorsal fin, is normally equipped with 10 spines, although 9 or 11 spines are sometimes observed, and it is broadly connected to the soft dorsal fin. The anal fin has three spines. The species’ most distinct characteristic is the red edge on the opercle (“ear”) flap of the male (orange on the female). The opercle flap is never greatly elongated as it is in species such as the redbreast sunfish (Lepomis auritus) or the longear sunfish (L. megalotis).
Author Archives: admin
Freshwater Drum
Aplodinotus is Greek for “single back”, and grunniens is Latin for “grunting”, referring to the fact that the species may be observed (or felt) making “grunting” sounds. Except for color, freshwater drum resembles its marine relative the red drum. The fish is deep-bodied and equipped with a long dorsal fin divided into two sections. The dorsal fin usually has 10 spines and 29-32 rays. Freshwater drum are silvery in color and lack the distinctive tail fin spot of red drum.
Carp
Cyprinus is Greek, and carpio is Latin; both words mean “carp.” The common carp is a heavy-bodied minnow with barbels on either side of the upper jaw. Typically, color varies from brassy green or yellow, to golden brown, or even silvery. The belly is usually yellowish-white. The dorsal fin with 17-21 rays, and the anal fin both have a heavy toothed spine. Individuals 12-25 inches in length and weighing up to 8-10 pounds are common, although they can grow much larger. Common carp may live in excess of 47 years and weigh over 75 pounds. The all-tackle world record was landed in 1987 from Lac de St. Cassien, France, and weighed in at 75 pounds 11 ounces.
Bluegill
Lepomis, the generic name, is Greek and means “scaled gill cover”. The species epithet macrochirus is also Greek and means “large hand” which may refer to the body shape or its size. Bluegills may be distinguished from other sunfish by the dark spot at the base of the dorsal fin, vertical bars on their sides, and a relatively small mouth. The spiny dorsal fin usually has 10 spines (but may have as many as 11 or as few as 9), and is broadly connected to the soft dorsal. The anal fin has three spines. The back and upper sides are usually dark olive green blending to lavender, brown, copper, or orange on the sides, and reddish-orange or yellow on the belly. Colors are more intense in breeding males, and vertical bars may take on a reddish hue.
Bass Fly
Stimulator
Largemouth Bass
Largemouth bass grow 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 cm) during their first year, 8 to 12 inches (20 to 30 cm) in two years, 16 inches (40 cm) in three years. They are usually green with dark blotches that form a horizontal stripe along the middle of the fish on either side. The underside ranges in color from light green to almost white. They have a nearly divided dorsal fin with the anterior portion containing nine spines and the posterior portion containing 12 to 13 soft rays. Their upper jaw reaches far beyond the rear margin of the eye.
Guadalupe Bass
Micropterus is Greek, meaning “small fin” and is a rather unfortunate misnomer arising from an injured type specimen that made it appear that the posterior rays of the soft dorsal fin formed a small separate fin. Treculi refers to Trecul, the French compatriot of Vaillant and Bocourt. Trecul actually caught the specimen. The Guadalupe bass is generally green in color and may be distinguished from similar species found in Texas in that it doesn’t have vertical bars like smallmouth bass, its jaw doesn’t extend beyond the eyes as in largemouth bass, and coloration extends much lower on the body than in spotted bass.